Santa Cruz is an area of geologic interest with a complex history of processes that shaped the coastline, bluffs, terraces, and mountains we see today! Wind, waves, earthquakes, fires, and other natural forces have changed and shaped the landscape for millions of years, though humans have only been able to document those changes in the recent past.
Jump To: Formations | Rock Types | Minerals | Resources
Geologic Formations
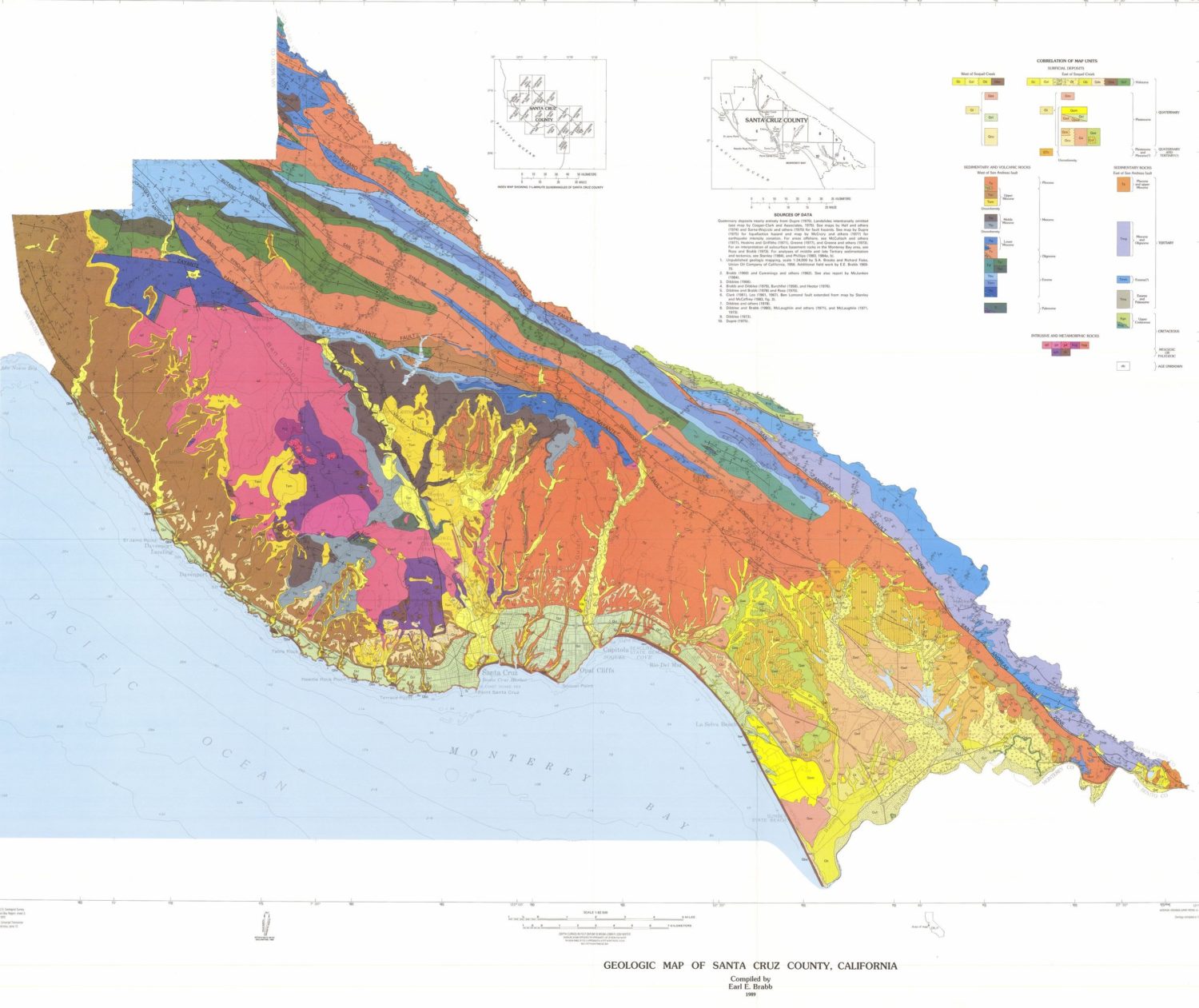
The above map shows the distribution of different rocks in Santa Cruz County. Each color represents a different kind of rock and, in turn, a particular age. Many of these rocks represent formations.
A geological formation is a basic rock unit that geologists use to group rock layers. Each formation must be distinct enough for geologists to tell it apart from surrounding layers and identify it on a map. A formation can consist of a variety of related or layered rocks, rather than a single rock type. There are over 14 geologic formations in Santa Cruz County. Most of these formations were created through movement of the crust because of tectonic uplift at the subduction zone off the California coast.
Most of the county is underlain by granitic rock. It formed about 100 million years ago from molten rock which cooled very slowly at a depth several miles below the earth’s surface. Since then, this area has been covered by the sea much of the time. Sand, mud and other sediment was deposited on the seafloor and was eventually compressed and hardened into sedimentary rock which was uplifted to form the Santa Cruz Mountains. Many of the sedimentary beds, which were originally horizontal, have been tilted, folded or partly eroded away. In some areas major faults have offset the rocks.

3 formations are known for fossils in this region:
Purisima Formation (3-7 Ma)
Santa Cruz Mudstone (7-9 Ma)
Santa Margarita Formation (10-12 Ma)
Learn more in our Fossil Guide.
Rock Types of Santa Cruz County
The three basic types of rocks — igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary — occur in Santa Cruz County. All are composed of minerals. Some consist of primarily one mineral, as in the case of marble, while others are an aggregate of many different minerals, as in the case of granite and conglomerate.
Each rock type in the Santa Cruz area represents a different chapter in this region’s geologic past, and each has its own unique story to tell. The rocks of this area are mostly covered by soil and vegetation, so geologists must rely on scattered outcrops in creek beds, quarries, road cuts and sea cliffs in order to piece together the geologic history.
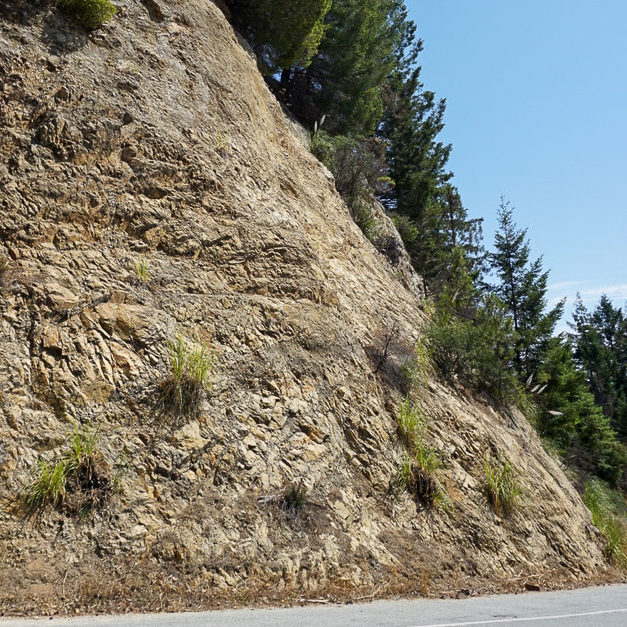

Igneous rocks formed from molten rock called magma. Plutonic rocks, such as granite, gabbro and alaskite, cooled very slowly, solidifying deep below the earth’s surface. This provided time for larger crystals of quartz, feldspar, mica and other minerals to form, giving the rocks a coarse texture. Volcanic rocks, such as basalt, cooled quickly at the earth’s surface and are very fine grained.
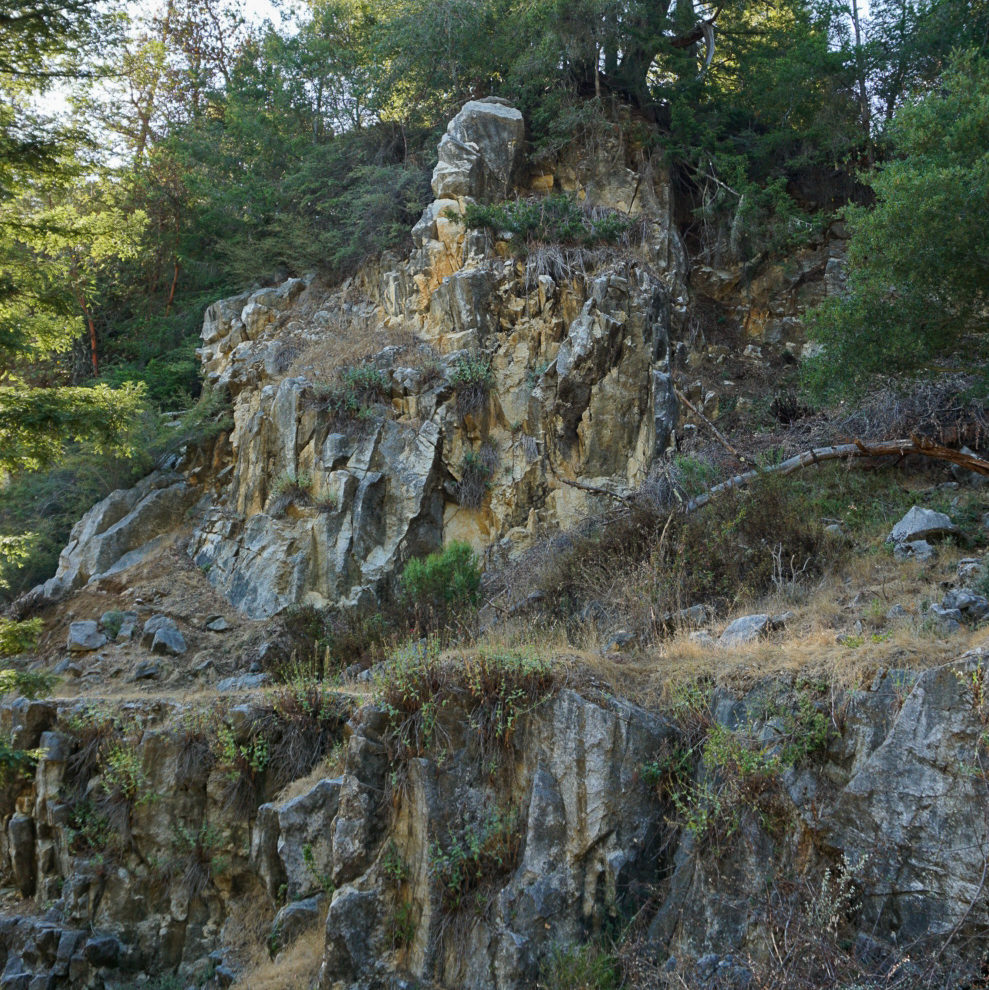

The metamorphic rocks of this area are a geological enigma. They predate the granite rocks and were originally sedimentary rocks such as limestone, shale and sandstone. These were respectively metamorphosed into marble, schist and quartzite by the intrusion of magma about 100 million years ago. How much earlier these rocks were laid down as sediment, however, remains a mystery.
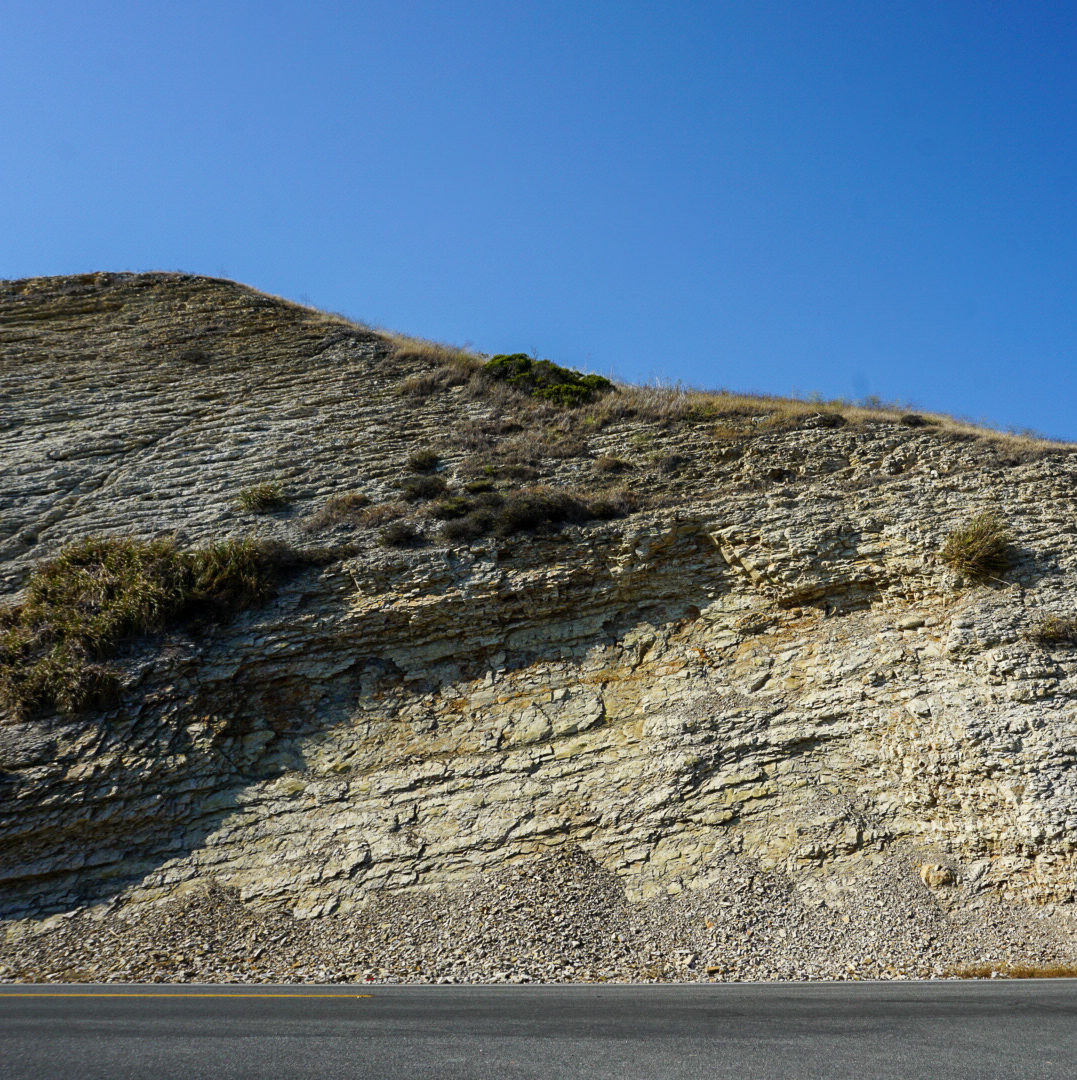

Sedimentary rocks in the Santa Cruz area originated for the most part from sediment such as mud, sand and gravel that was deposited on the sea floor. Over millions of years chemical alteration and pressure from burial hardened the sediment into rock. These rocks overlie the igneous and metamorphic rocks of this region and are of a younger age.
Minerals
Minerals are the naturally occurring crystalline substances that make up the rocks around us. Minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and calcite are the most common constituents of rocks in this area. Dozens of other mineral species occur here, but in small amounts. Large, well-formed crystals- the kind most sought after by collectors- are scarce.
Several minerals in this region have proven to be of great economic importance. Cinnabar (the chief ore of mercury) has been mined extensively at the New Almaden on the east slope of the Santa Cruz Mountains. Calcite (in the form of marble) has long been quarried near Santa Cruz for the manufacturing of lime and cement.
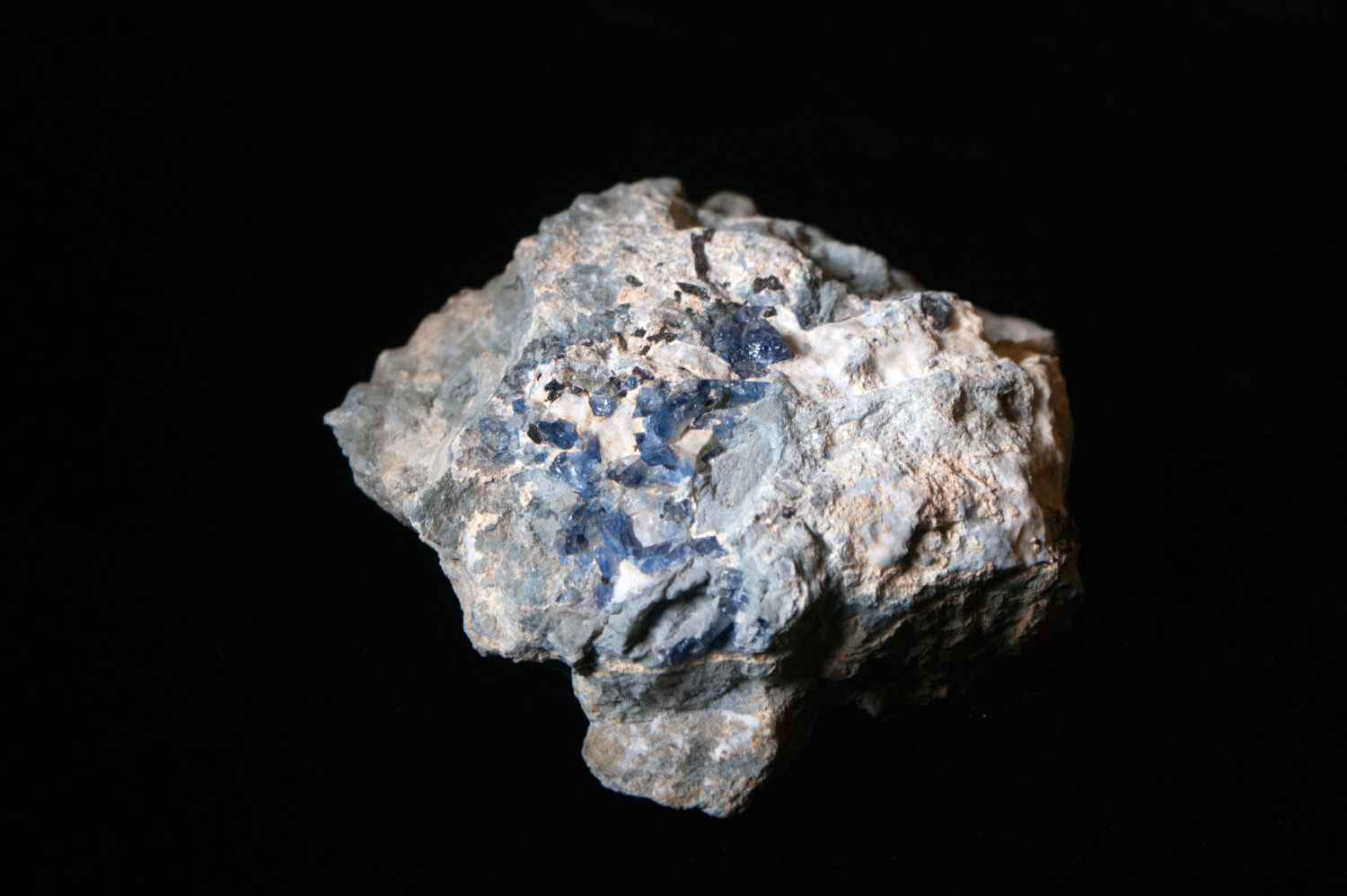

Benitoite is the California state mineral. This unusual blue crystal was first discovered in 1907 in San Benito County. While benitoite is found in a few places around the world, San Benito County is the only place in the world where gem quality benitoite crystals are found.
Learn more in our Collections Close-Up.
Resources
Explore other resources for better understanding geology, paleontology, and the landscape of the Santa Cruz region.
Explore Online Rock Resources
- READ: Rock Record blog – Musings on the Mineral World from Gavin Piccione and Graham Edwards
- WATCH: Rockin’ Pop Ups – short programs on geologic topics with the Geology Gents
- READ: A Guide to the Fossils of Santa Cruz County
- READ: Collections Close-Up: Laura Hecox’s Rocks
- WATCH: Collections Close-Up: Benitoite with Hilde Schwartz
- WATCH: Fire and Mud: Why Fires Cause Debris Flows in California with Noah Finnegan
- WATCH: Ten Years Since the Tsunami with the UCSC Seismology Lab
- WATCH: Loma Prieta +30 Lecture with Frank Perry
- ACTIVITY: Geology of Westcliff Drive Tour
- ACTIVITY: Santa Cruz Geologic Top 5 Must-Sees
Books and Papers
- Fossil Invertebrates and Geology of the Marine Cliffs at Capitola, California by Frank Perry
- Fossil Sharks and Rays of the Santa Cruz Mountains by Frank Perry
- Roadside Geology of Northern and Central California by David Alt and Donald W. Hyndman
- Rockhounding California by Gail A. Butler
- The Edge: The Pressured Past and Precarious Future of CA’s Coastline by Kim Steinhardt and Gary Griggs
- Santa Cruz Coast: The & Now by Gary Griggs and Deepika Shrestha Ross
- Stratigraphy, paleontology, and geology of the central Santa Cruz Mountains, California Coast Ranges by Joseph C. Clark, 1981
Geology at the Museum
On exhibit at the Museum
- Specimens of common minerals from the region
- Specimens of common rocks from the region
- A detailed topographic geologic map of the county
- Garden: Take a stroll around the Museum’s Garden Learning Center and see if you can spot fossils and other large rock samples.
- Activities for kids: Multiple dig boxes features Santa Margarita Formation fossils of sand dollars and casts of a fossil sea cow.
Bring rocks home
Rent a kit to explore local rocks at home. Kit rentals are $10 per week and can be requested here (you do not need to be a teacher to request a rental).